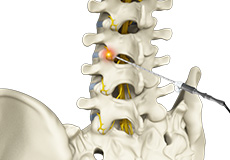
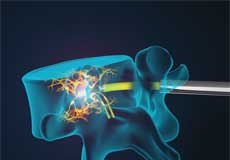
Spine
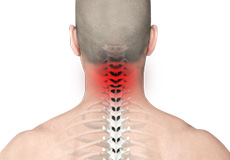
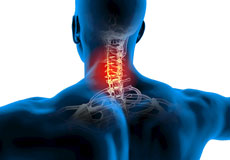
Neck Pain
Common neck pain may occur from muscle strain or tension from everyday activities including poor posture, prolonged use of a computer and sleeping in an uncomfortable position.
Degenerative Disc Disease
Degenerative disc disease (DDD) refers to the gradual deterioration of the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae. DDD is a misnomer as it is not actually a disease but a condition that affects the strength, resilience and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to advancing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture or poor body mechanics.
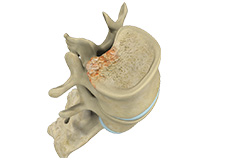
Spinal Infection
A spinal infection is described as an infection of the spine. It can occur in various locations of the spine i.e., intervertebral disc space, vertebral column, spinal canal, and nearby soft tissues.
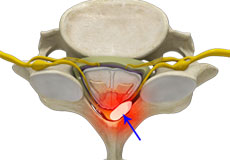
Spinal Tumors
A spine tumor is the abnormal growth of uncontrolled tissues or cells in and around the spinal cord. Tumors can either be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign). Tumors that begin in the spine are called primary spinal tumors.
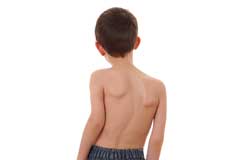
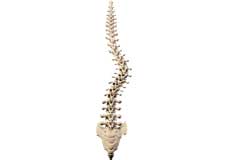
Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine that causes a deviation to one side. It causes a physical deformity, making the spine look like the letter “C” or “S” instead of the letter “I”. Scoliosis can affect either the mid or lower back. Scoliosis of the mid back is more common. Scoliosis can occur at any age.
Kyphosis
Kyphosis is a condition of abnormal curvature of the spine that causes rounding of the upper back or a hunchback. The thoracic portion of the spine normally has a C-shaped curve, but excessive forward curve in the spine leads to kyphosis. Kyphosis most commonly affects the thoracic spine, but can involve the cervical and lumbar portions too.
Osteoporotic Fractures
Osteoporosis is a bone disorder where your bones become fragile and weak causing them to break easily. The condition occurs when your body starts losing bone or does not make enough bone or both, due to calcium deficiency.
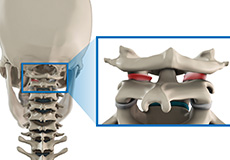
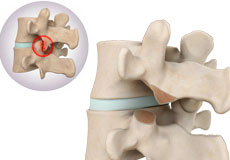
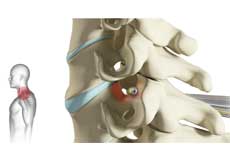
Facet Joint Arthritis
Facet joints, also called zygapophyseal joints, are synovial joints located at the back of your spine, connecting the vertebrae together. Normally the facet joints are lined by a cartilage and a membrane of synovium. There are two joints between each pair of vertebrae located on either side of the spine. The facet joints provide stability for the spine.
Sciatica
Sciatica is a painful condition caused by the irritation of the sciatic nerve. Sciatica can be acute (short term), lasting for a few weeks or chronic (long term), persisting for more than 3 months. It is important to understand that in most cases, sciatica will resolve itself within a few weeks or months and rarely causes permanent nerve damage.
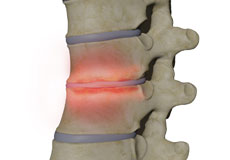
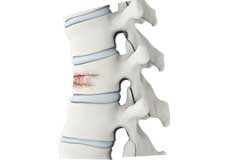
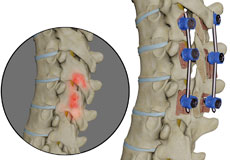
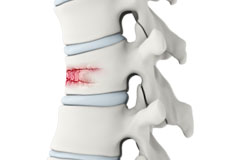
Spinal Fractures
Vertebral compression fractures occur when the normal vertebral body of the spine is squeezed or compressed. The bone collapses when too much pressure is placed on the vertebrae, resulting in pain, limited mobility, loss of height, and spinal deformities.
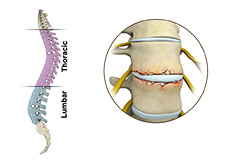
Spine Disorders
The spine is made up of a column of small bones called vertebrae that surround and protect the spinal cord and nerves that branch out from the spinal cord. Each bone or vertebra is separated from the other by a spongy tissue called an intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushion and prevents the bones from rubbing against each other during movement.
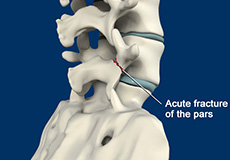
Spondylolysis
Spondylolysis is a stress fracture in the vertebra that may progress into spondylolisthesis, a condition where the vertebra gets displaced from the spinal column. Spondylolysis is the cause of frequent low back pain in children. It is more common among children and teenagers who participate actively in sports such as football, weightlifting, and gymnastics.
Spinal Instability
Spinal instability refers to the condition of failure of the spinal column to maintain its normal structure. Normally, the spine functions to protect and provide support to the body and its internal organs. An unstable spine is incapable of holding various spinal structures such as spinal muscles, ligaments, bones, and discs in place.
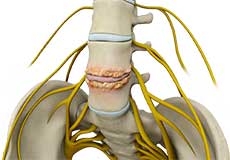
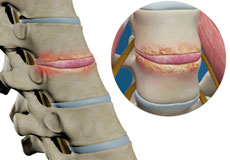
Spondylodiscitis
Spondylodiscitis is an infection of the intervertebral discs (between the vertebrae) along with the vertebrae (one of many small bones forming the spine). The condition is a primary infection of one or more intervertebral discs (discitis) with secondary infection of one or more vertebrae (spondylitis).
Spine Deformities
The spine or backbone provides stability to the upper part of our body. It helps to hold the body upright. It consists of a series of irregularly-shaped bones appearing in a straight line. The spine has two gentle curves, when viewed from the side and appears to be straight when viewed from the front.
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is the displacement of the vertebral disc from the spinal column. Outward (forward) displacement is termed as anterolisthesis and inward (backward) displacement is termed as retrolisthesis. This condition is often preceded by spondylolysis, a degenerative condition of the vertebra.
Spondyloarthropathies
Spondyloarthropathies are a group of chronic inflammatory diseases of the spine and joints. Spondyloarthropathies can occur at any age, however, they occur more often in young males.
Isthmic Spondylolisthesis
Isthmic spondylolisthesis is a spinal disorder in which one vertebra glides forward over the vertebra below. It usually affects the lumbar (lower back) spine, more frequently at L5-S1 levels (the fifth lumbar vertebra and first sacral vertebra).
Spine Trauma
Spine trauma is defined as an injury or damage to any region of the spine. The spine extends from the neck to the lower back and consists of the vertebral bones which surround and protect the spinal cord. Damage to the spinal cord or spinal nerves can cause changes in sensation, strength, and other body functions.
Peripheral Nerve Compression
The human body has 2 nervous systems, the central nervous system that includes the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system that includes a network of nerves that lie outside the brain and spinal cord.
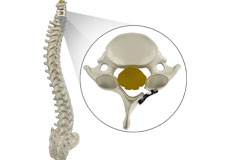
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a condition caused by the vertebral column constricting and exerting pressure on the spinal cord or neural foramen (a bony tunnel through which a nerve exits the spinal cord).
Neck Strains and Sprains
The neck is the most flexible part of the spine and supports the weight of the head. The unique anatomical structure of the cervical vertebrae allows the free movement of the head. The neck is also composed of muscles and ligaments. Any excessive stress on the ligaments and muscles may injure or damage them.
Spinal Compression Fractures
A compression fracture of the vertebra occurs when the bones of the spine (vertebrae) collapse. Most commonly, these fractures occur in the thoracic or the middle portion of the spine.
Spinal Injuries at Work
Injuries at the workplace are very common and may be debilitating. Global statistics report that around 260 million non-fatal injuries occur every year around the world of which 350,000 cases may suffer death. Workplace injuries often occur because of high-risk jobs, lack of or scarcity in safety devices, lack of training, and higher numbers of manual workers.
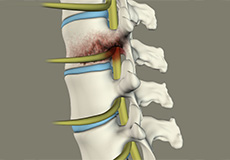
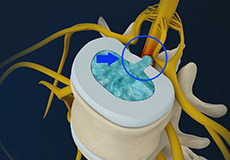
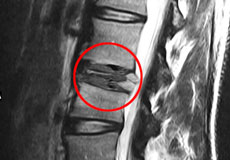
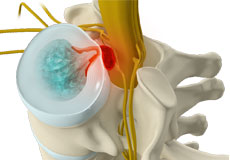
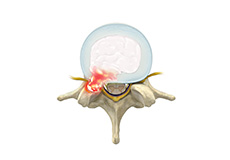
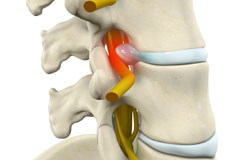
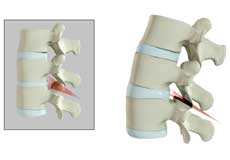
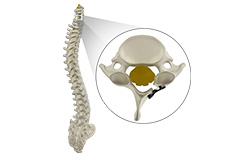
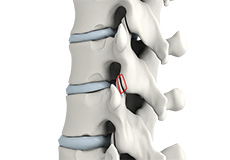
Disc Herniation
Disc herniation is a condition where the central nucleus pushes through the outer edge of the disc, causing a bulge that compresses the spinal nerves.
Vertebral Compression Fractures
Back pain is an indication of stress fractures known as vertebral compression fractures. Vertebral compression fractures occur when the normal vertebral body of the spine is squeezed or compressed. The bone collapses when too much pressure is placed on the vertebrae, resulting in pain, limited mobility, loss of height and spinal deformity.
Degenerative Spinal Conditions
A degenerative condition is a continuous deterioration of a tissue or an organ in your body over time. Degenerative spinal conditions refer to a gradual loss of normal structure and/or function of the spine over time.
Scheuermann's Kyphosis
Scheuermann’s kyphosis is a deformity of the spine that develops during growth. It can be considered as increased kyphosis. Kyphosis is the C-shaped curving of the spine and is also known as hunchback. This deformity occurs in the junction between the thoracic region and lumbar sections of the spine or in the chest region.
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Sacroiliac joint dysfunction or sacroiliac joint pain is one of the common causes of low back pain.
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Sacroiliac joints are present in the lower back where the sacrum part of the vertebrae joins the iliac bones. The term ankylosis stands for loss of mobility of the spine, whereas spondylitis means inflammation of the spine.
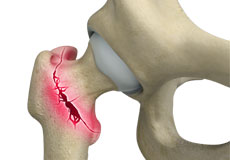
Pathological Fractures of the Spine
Pathological fractures are broken bones in an area already weakened by another disease, not by an injury. Some underlying diseases can weaken the spinal bones making them brittle and eventually causing a fracture or break in the bone.
Difficulty Walking
Walking is a complex interaction among multiple systems of the body. Proper walking is a result of balance, sensory function, reflexes, motor function, and many other systems working in conjunction.
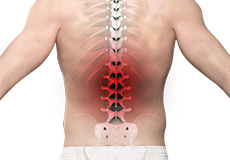
Low Back Pain
Low back pain is often a common symptom of many disease conditions and the back pain may range from simple or dull pain to sudden and sharp pain. If the pain persists for a few days, it is acute pain whereas if it continues for more than 3 months, it is considered as chronic pain.
Poor Balance
Poor balance can be defined as a sense of unsteadiness on your feet due to dizzy spells or lightheadedness, fainting, blackouts, or loss of consciousness.
Epidural Abscess
An epidural abscess is a medical condition that can be defined as an infection in the region between the spine, or bones of the skull, and the membranes that surround the spinal cord (meninges) and brain.
Spine Bone Spurs
Spine bone spurs, also called osteophytes, are bony projections that develop in the spine’s facet joints where cartilage has worn out or along the vertebral body’s endplates edges. It can grow at any level of the spinal column such as the low and mid-back and in the neck.
Whiplash
Whiplash is a soft tissue injury to the neck, usually caused by a sudden forceful jerk commonly occurring because of an automobile accident, sports injuries or an accidental fall. Headache may develop immediately or after a short period of time after the injury. Sometimes, whiplash may also be referred to as neck strain, neck sprain or hyperextension injury.
Adult Degenerative Scoliosis
Adult degenerative scoliosis is characterized by side to side or lateral bending of the spine in adults. Degenerative scoliosis can involve either the mid-back and/or lower back region of the spine.
Pseudarthrosis/Nonunion
Pseudarthrosis is an unhealed broken bone, also known as nonunion. Usually, damaged or broken bones heal over time by forming new bone tissue connecting the damaged pieces of the bone. However, if the damaged bone fails to heal then it is called ‘nonunion’ or ‘pseudarthrosis’.
Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis (DISH) is a condition that commonly affects the spine. It is characterized by calcification (bony hardening) of ligaments, tendons and joint capsule insertions. Usually, the upper portion of the back (thoracic spine) is affected, but it may also involve the neck (cervical spine) and lower back (lumbar spine).
Cauda Equina Syndrome
What Cauda equina syndrome is an emergency condition characterized by persistent severe lower back pain caused by the compression of a bundle of spinal nerves (cauda equina) at the end of the spinal cord (lower back and hip region).
Chiari Malformation
Chiari Malformation (CM) is a condition in which the brain tissue extends into your spinal canal. This occurs when part of your skull is abnormally small or misshapen, causing it to press on the brain and forcing it downward.
Discitis
Discitis, also called discitis, is inflammation between the spaces of the intervertebral discs in the spine. Intervertebral discs are located between the vertebrae and spaces between them are called intervertebral disc spaces. Swelling in these spaces puts pressure on the discs and results in pain.
Disc changes
The cartilaginous disc is made up of an outer fibrous layer called the annulus fibrosus, which surrounds an inner gelatinous core called the nucleus pulposus. The nucleus pulposus is well hydrated and acts as a shock absorber.
Mid-back Pain
Mid-back pain is also called as thoracic pain or upper back pain. It occurs at the back of the chest and is much less common than lower back pain. It may occur due to poor posture, muscle strain, improper lifting and bending, physical inactivity, sports injury, a trauma in a car accident, cancer, or an autoimmune disease.
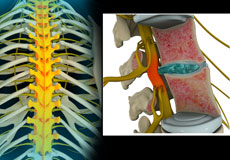
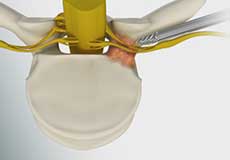
Radiculopathy
Radiculopathy is a condition where a nerve root in the spine is compressed, producing pain or weakness across the whole length of the nerve. It is sometimes referred to as a pinched nerve or sciatica. It occurs most commonly, but is not limited, to the lower back and neck.
Back Pain in Children
Back pain is uncommon in children and is usually associated with a serious underlying condition or an injury. Often, the cause of back pain is non-specific and is thought to be due to musculoskeletal strain, poor posture, heavy school bags that are not worn correctly or underlying mood problems.
Osteoporosis of the Spine
Osteoporosis is a bone disease characterized by a decrease in bone mass and density resulting in brittle, fragile bones that are more susceptible to fractures. The condition most commonly affects elderly women. Osteoporosis-related fractures are more common at the vertebral bodies of the spine.
Adult Kyphosis-Types and Causes
Postural kyphosis is the result of poor posture and is common in adolescents and younger adults. Slouching posture when sitting or standing tends to cause the spine to curve forward.
Idiopathic Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine, either to the left or to the right. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a type of scoliosis that occurs in children between 10 and 16 years of age.
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Scoliosis is a medical condition characterized by an abnormal lateral curvature of the spine, either to the left or to the right. Adolescent idiopathic scoliosis (AIS) is a type of scoliosis that occurs in children between 10 and 16 years of age.
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome
Failed back surgery syndrome is a term used to describe poor results from previous spine surgery.
Cervical Disc Herniation
Cervical disc herniation can arise due to aberrations of the intervertebral disc such as bulging, rupture, and slipped or extruded disc. It results in neck, shoulder, and arm pain. In some cases, a disc herniation may occur due to injury, repetitive movements, or degenerative disc disease (DDD).
Cervical Radiculopathy/Myelopathy
Disc protrusion, also called herniated disc, is a condition caused by a tear in an intervertebral disc, allowing the disc contents to bulge out.
Cervical Fracture
Cervical fractures are common in motor vehicle accidents, sports activities and falls. The second, sixth and seventh cervical vertebrae are frequently involved in fractures, which may injure the spinal cord.
Cervical Spondylosis
Cervical spondylosis, also called arthritis of the neck, is an age-related medical condition characterized by deterioration of spinal joints, vertebrae, discs, and ligaments in your neck.
Cervical Degenerative Disc Disease
Cervical degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a misnomer, as it is not a disease as such but a condition that affects the strength, resiliency and structural integrity of the intervertebral discs due to increasing age, trauma, injury, repetitive movement, improper posture, or poor body mechanics.
Cervical Deformities
The spine is made up of 33 small bones called vertebrae and is known as the spinal column or vertebral column. It can be divided into 5 parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacral, and coccyx region. The cervical spine is comprised of the first 7 vertebrae, which supports the neck and the head.
Cervical Stenosis
Cervical stenosis refers to the narrowing of the spinal canal that protects the spinal cord and its branching nerves.
Cervical Disc Protrusion
Cervical disc protrusion, commonly known as a disc bulge, occurs when the spinal discs and associated ligaments are intact, but may form an outpouching that presses on the spinal nerves.
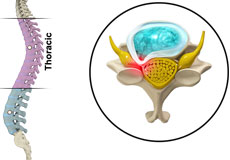
Thoracic Disc Herniation
Thoracic herniation disc is a condition in which the outer fibers (annulus) of the intervertebral disc are damaged causing the soft inner material of the nucleus pulposus to rupture out of its space. This condition can be extremely serious if it occurs in the thoracic spine. Thoracic disc herniation is a relatively uncommon condition.
Thoracic Myelopathy
Thoracic myelopathy is a disorder resulting from severe spinal cord compression in the thoracic region. The spinal cord in this region typically gets compressed as a result of bulging or herniated discs, spinal trauma, or bone spurs causing severe pain and discomfort. Thoracic decompression surgery is one of the effective ways to treat thoracic myelopathy.
Fracture of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
The backbone is made of small bones arranged from the neck down to the buttocks, one above the other. The region at the chest and lower back are called the thoracic and lumbar spine, respectively. These are the two regions commonly affected by a fracture.
Thoracic Nerve Compression
Thoracic nerve compression refers to a compressed nerve root in the thoracic region of the spine, also called the upper back.
Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation is the most common cause of lower back pain and leg pain (sciatica). Aging, injury or trauma may cause the annulus fibrosus to tear, resulting in protrusion of the nucleus pulposus. This may compress the spinal nerves and/or spinal canal.
Lumbar Stenosis
Lumbar stenosis is the compression of spinal nerves caused by the narrowing of the spinal canal. It is one of the common causes of lower back pain. Spinal stenosis can also affect the spine in the neck region.
Lumbar Degenerative Disc Disease
Lumbar degenerative disc disease (DDD) is a common cause of lower back pain. Over time, these natural shock absorbers wear out and degenerate. Degenerative disc disease is not actually a disease but refers to the changes in the spine that occur as a part of the normal aging process.
Lumbar Radiculopathy
Back pain is a common condition affecting approximately 80% of the population at some point in their lives. The area usually affected is the lower back (lumbar region) as it bears most of the upper body’s weight. Trauma to the spine, age and overuse can result in deterioration of the vertebral bones and joints or bulging of the discs.
Lumbar Facet Joint Arthropathy
A joint is a place where two bones contact each other. Arthropathy means any disease of the joints. Lumbar facet joint arthropathy occurs when the facet joints degenerate or wear out over time due to aging or arthritis.
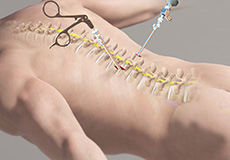
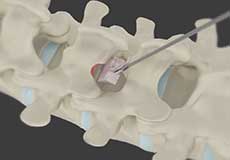
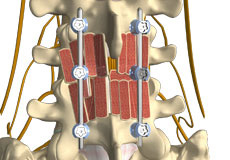
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery
Minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) is the latest technology available to perform spinal surgeries through small, less than one-inch-long incisions. It involves the use of special surgical instruments, devices and advanced imaging techniques to visualize and perform the surgery through such small incisions.
Revision Spinal Surgery
Revision spine surgery is surgery performed in certain patients to correct the problems of earlier spine surgery.
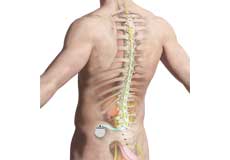
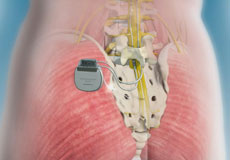
Spinal Cord Stimulator
A spinal cord stimulator is a device that sends electrical impulses to the areas of the spinal cord causing pain and interferes with the transmission of pain signals to the brain. It blocks the brain's ability to sense pain in the stimulated areas, thus relieving pain without the side effects that medications can cause.
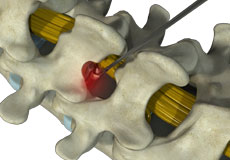
Kyphoplasty
Balloon kyphoplasty is a spine surgery that relieves back pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture. The aim of balloon kyphoplasty is to relieve pain, stabilize the fracture and restore the vertebral body height.
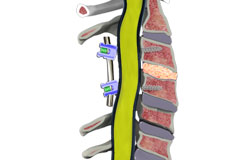
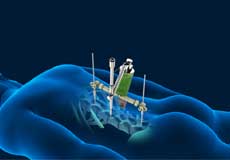
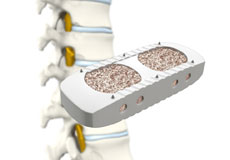
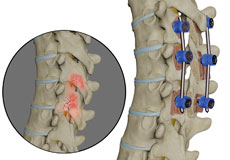
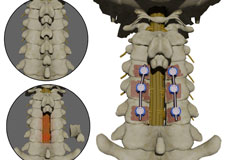
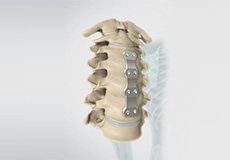
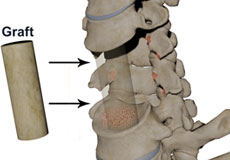
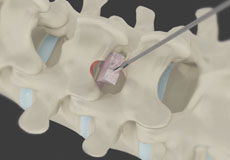
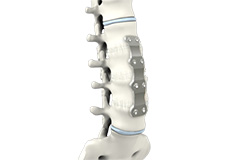
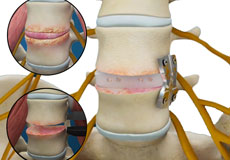
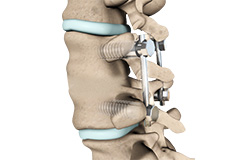
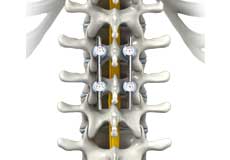
Spinal Fusion
Spinal fusion is the surgical technique of combining two or more vertebrae. A fusion of the vertebrae involves the insertion of secondary bone tissue obtained either from an autograft (tissues from your own body) or allograft (tissues from another person) to enhance the bone healing process.
Spinal Decompression
Spinal decompression is a treatment to relieve pressure on one or many “pinched nerves” in the spinal column. It can be achieved either surgically or by non-surgical methods. Spinal decompression is used to treat conditions that cause chronic backaches such as herniated disc, disc bulge, sciatica, and spinal stenosis.
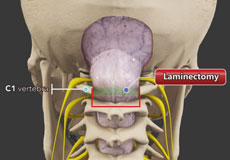
Laminectomy
Laminectomy refers to the removal or cutting of the lamina (roof) of the vertebral bones to provide space for the nerves to exit from the spine. It can also be performed to relieve the symptoms of the narrowed spinal canal known as spinal stenosis.
Vertebroplasty
Vertebroplasty is a minimally invasive procedure performed to reduce or eliminate pain caused by a vertebral compression fracture. It stabilizes the fracture and prevents further collapse of the vertebra, averting deformity.
Foraminoplasty
Neural foramina are small canals at every level of the spine through which nerves leave the spinal cord and go to the limbs and other parts of the body. Narrowing of this canal is called foramina stenosis. The narrowing may be caused by bone spurs, a herniated or bulging disc, arthritis, ligament thickening or enlargement of a joint in the spinal canal.
Scoliosis Treatment
Scoliosis is the abnormal curvature of the spine giving the spine an “S” or “C” shape. Scoliosis can occur at any age and is more common in girls than boys. Larger curves cause discomfort while the smaller curves do not cause any problems. In most cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Scoliosis Surgery
Surgery for scoliosis is recommended when the spinal curvature is severe and is either worsening or is a cause of severe pain or difficulty in breathing. The surgery is aimed at rectifying the spinal curvature, stabilizing the spine and preventing it from worsening.
Spine Deformity Surgery
Spine deformity can be defined as abnormality in the shape, curvature, and flexibility of the spine. When the curves are exaggerated, pronounced problems can occur such as back pain, breathing difficulties and fatigue.
Spinal Manipulation
Spinal manipulation is a non-surgical "hands-on" technique in which professional chiropractic specialists use leverage and exercises to adjust spinal structures and restore mobility of the back. During pain, the nerve that is interconnected with the muscles, joints, bone becomes weak and loses its ability to function.
Spinal Tumor Surgery
A spinal tumor is an abnormal mass of tissue surrounding or found within your spinal cord and/or spinal column.
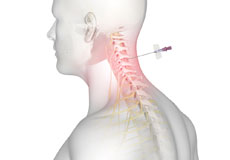
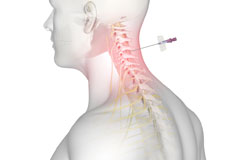
Neck Surgery
Neck surgery is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of neck pain when conservative measures such as physical rehabilitation, medications, and rest have failed to provide any relief to your neck pain.
Robotic Spine Surgery
Robotic spine surgery is a procedure where your surgeon is assisted by a robotic system to perform surgery to the spine. Precision is very important when performing spine surgery.
Sacroiliac Joint Minimally Invasive Fusion
Sacroiliac (SI) joints are joints in the lower back region, where the sacrum and ilium bones join. Although these joints are small and have limited motion, they play an important role in connecting your spine to the pelvic bone and lower part of your body. They perform an important function in absorbing shock from the upper portion of your body.
Kyphoplasty and Vertebroplasty
Osteoporosis is a “silent” disease characterized by the weakening of bones. This makes the patients more susceptible to fractures, typically in the hip and spine. The elderly and post-menopausal women are at a greater risk of developing osteoporosis.
Lateral Extracavitary Approach Surgery
Many approaches have been introduced in spinal surgery to gain optimal access to the injured or diseased area, with minimal or no damage to surrounding tissues. There are three main approaches – anterior (from the front), posterior (from the back) and lateral (from the side).
Posterior Scoliosis Surgery
The goal of scoliosis surgery is to both reduce the abnormal curve in the spine and to prevent it from progressing further and getting worse. To achieve this, a spinal fusion is performed to fuse the vertebrae within the curve to be corrected. This involves placing bone graft or bone graft substitute in the intervertebral space between the two vertebrae.
Scoliosis Correction with Spinal Monitoring
Scoliosis is a condition characterized by the abnormal curvature of the spine. The abnormality can be surgically corrected by fusing the affected parts of the spine so that they grow into a solid bone and do not twist. During the surgery, your doctor makes an incision to expose the spine.
How to prevent Back Pain
Back pain is common and usually affects everyone at some point. It often occurs more frequently as you grow older. Pain can either be sharp and sudden or dull and constant. Acute back pain lasts a few days or weeks while pain that lasts more than 6 months is considered chronic.
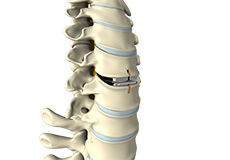
Discography
Discography or a discogram is a procedure to evaluate back pain. It helps identify a painful spinal disc.
Endoscopic Spine Surgery
Endoscopic spine surgery is a minimally invasive spine surgery that uses specialized video cameras and instruments to remove the herniated disc through very small incisions.
Removal of Facet Joint Cyst
Facet joint cysts, also called synovial cysts, are benign, fluid-filled sacs that develop due to degeneration of the facet joints of the spine. These cysts normally occur in the lumbar spine (lower back) area and may not cause problems, but when large enough, they can cause spinal stenosis or narrowing of the spinal canal leading to compression of the spinal cord or spinal nerves.
Transpedicular Approach Surgery
The vertebral column is made up of individual bones (vertebrae) stacked one above the other. These are protected by spongy intervertebral discs that cushion the spine during movements such as lifting, running, and jumping.
Treatment Options for Back and Neck Pain
Back and neck pain is common symptoms of injury, damage, deformity, or unhealthy spinal conditions. Pain may range from a mild ache to a sharp shooting pain that can spread down your arms and legs. There are many conservative and surgical treatment options that can relieve pain by targeting the symptoms or the underlying problem.
XLIF - Extreme Lateral Interbody Fusion
Extreme lateral interbody fusion (XLIF) is a minimally-invasive surgery that involves the fusing of two degenerative spinal vertebrae. The procedure is conducted to relieve painful motion in the back caused by spinal disorders.
Sacroiliac Joint Arthrodesis
Sacroiliac (SI) joint arthrodesis is a surgical procedure employed for the treatment of sacroiliac joint dysfunction and/or inflammation/pain. The procedure involves surgical immobilization of the SI joint by fusion of the sacrum and ilium bones using instrumentation, bone graft, or both.
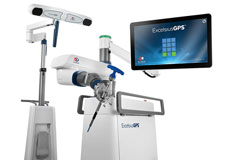
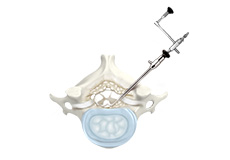
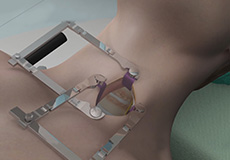
ExcelsiusGPS Robotic Navigation
ExcelsiusGPS® Robotic Navigation system is the latest technology designed to integrate the benefits of robotics and navigation into one platform to provide minimally invasive spine surgery and optimize patient care with improved accuracy and safety.
Surgery for Scoliosis
Surgery for scoliosis is recommended when the spinal curvature is severe and is either worsening or is a cause of severe pain or difficulty in breathing. The surgery is aimed at rectifying the spinal curvature, stabilizing the spine and preventing it from worsening.
Spine Osteotomy
Spine osteotomy is a surgical procedure in which a section of the spinal bone is cut and removed to allow for correction of spinal malalignment.
Fracture Stabilization
A spinal fracture refers to a break in any of the bones that make up the spine. It can occur due to trauma such as a traffic accident, fall from a significant height or weakening of the bones due to osteoporosis or a tumor. The thoracic or lumbar spine (upper and lower back) are the most common locations for spinal fractures.
Spinal Infection Debridement
The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae which surround and protect the spinal cord. These are separated by intervertebral discs which provide cushioning between the vertebral bones. A spinal infection may affect any part of your spine, i.e. the vertebral column, intervertebral discs or the soft tissues surrounding the spine.
Spinal Infection Decompression
The spine is made up of bones called vertebrae which surround and protect the spinal cord. These are separated by intervertebral discs which provide cushioning between the vertebral bones. A spinal infection may affect any part of your spine including the vertebral column, intervertebral discs or the soft tissues surrounding the spine.
Spinal Infection Stabilization
The spine is made up of many bones called vertebrae which surround and protect the spinal cord. Intervertebral discs between the vertebral bones provide cushioning. A spinal infection may affect any part of the spine including the vertebral column, intervertebral discs or the soft tissues surrounding the spine.
Complex Spinal Surgery
Complex spine surgery is a type of back surgery involving a fusion of six or more vertebrae. The vertebrae are a series of small interlocking bones extending from the skull to the pelvis (hip) to form your spinal column or backbone. Spinal fusion helps in forming a solid bridge of bone that stabilizes your back.
Disc Decompression
Acute or chronic injury can cause a spinal disc to herniate or rupture. The damaged disc may compress against the spinal cord or the nerves that branch out through the vertebral bones, leading to pain, loss of sensation and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the nerve.
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA), also called rhizotomy or neurotomy, is a novel non-surgical technique of treating pain. This technique employs radiofrequency waves to produce heat and the heat produced damages the nerves transmitting pain signals to the brain.
Outpatient Spine Surgery
Outpatient spine surgery is an operative procedure that does not require an overnight stay at the hospital. It is also called ambulatory or same-day surgery. Improvement in surgical techniques, modern pain management, and rehabilitation protocols allows surgeons to perform certain operative techniques of the spine (from cervical to lumbar region), with a minimally invasive technique on an outpatient basis.
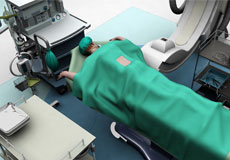
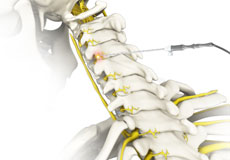
Image-Guided Spine Surgery
Imaging techniques such as computed tomography and fluoroscopy may be integrated into the system to facilitate pre-operative planning of the surgery, where a series of images taken before the surgery are displayed on a screen, with which your surgeon matches his/her moves intraoperatively.
Intracept - Basivertebral Nerve Ablation
Intracept is a minimally invasive procedure developed by Relievant to treat chronic low back pain by targeting the basivertebral nerve.
Minimally Invasive Discectomy and Decompression
The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. However, many conditions can cause parts of the vertebrae to compress the spinal cord or the nerves that branch out through them, leading to pain, loss of sensation and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the compressed nerve.
Adult Scoliosis Correction
Adult scoliosis is the abnormal curvature of the spine giving the spine an “S” or “C” shape in a skeletally mature person. Larger curves cause discomfort while smaller curves usually do not cause any problems. In most cases, the exact cause remains unknown.
Anterior and Posterior Scoliosis Surgery
The spine is the backbone of the body. It naturally curves a little. This allows us to walk, move and balance ourselves properly. But some people have a spine that curves too much to one side. This condition is called scoliosis. In most cases, especially in children and adolescents, the cause of scoliosis is unknown and scoliosis is referred to as idiopathic scoliosis.
Surgical Treatment for Spine Conditions
Surgical treatment is the last resort for chronic backache when other therapies do not relieve the pain. Some surgical procedures can be performed as an out-patient procedure while others may require hospital admission. Surgical treatment is considered when there is damage to the peripheral nerves and the patient is suffering from a progressive neurologic disease.
Spinal Facet Rhizotomy
Spinal facet rhizotomy is a minimally invasive procedure to destroy nerves that transmit pain impulses from the facet joints of the spine.
Spinal Decompression Therapy
Spinal decompression therapy involves stretching your spine using a manual or motorized traction table to help ease neck, back, or leg pain. It is a non-surgical technique to relieve pressure on your spinal discs and spinal nerves. Spinal traction is also believed to improve the supply of blood, oxygen and nutrients to the spine to promote healing.
Minimally Invasive Scoliosis Surgery
The goal of scoliosis surgery is to both reduce the abnormal curve in the spine and to prevent it from progressing further and getting worse. To achieve this, a spinal fusion is performed to fuse the vertebrae, in the curve to be corrected.
Minimally Invasive Spine Surgery for Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a condition of the spine characterized by the forward displacement of a vertebra over an underlying vertebra. A significant displacement can cause a compression of the spinal nerves resulting in pain. The two most common types of spondylolisthesis include dysplastic spondylolisthesis and isthmic spondylolisthesis.
Neuromodulation
Pain is an unpleasant sensation caused by illness or injury. Pain can have a negative impact on a person's quality of life. Chronic pain is the pain that is constant and persists for long periods of time. The treatment options for chronic pain include medications, surgical interventions, physical therapy, and psychotherapy.
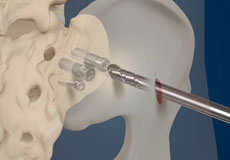
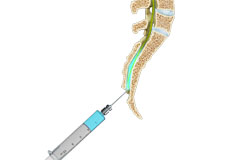
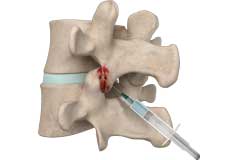
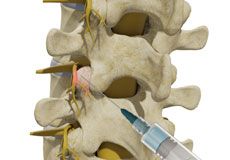
Transforaminal Epidural Block
Epidural blocks contain a strong anti-inflammatory agent called corticosteroid and an anesthetic for pain relief. It is administered into the epidural space of the spine, the space between the outermost covering of the spinal cord (dura mater) and the wall of the spinal canal.
Epidural Spinal Injection
Epidural spinal injection is a non-surgical treatment option utilized for relieving back pain. Spine degenerative conditions such as herniated disc, spinal stenosis and many others may induce back pain due to the compression of the associated spinal nerves.
Transforaminal Epidural Steroid Injection
The epidural space of the spine is the area between the vertebral bones and the protective dura sac that surrounds the spinal cord and nerves.
Medial Branch Block Injections
Facet joints are the joints connecting the different vertebrae of the spine to each other. Medial branch nerves are small nerves that supply the facet joints of the spine.
Caudal Epidural Injection
The epidural cavity is the space surrounding the spinal cord, which extends from the skull to the tailbone, and consists of fat, nerves and blood vessels. Nerves in this space can be blocked by injecting an anesthetic, or a constricted nerve can be relieved of pain and inflammation by injecting a steroid medication into the epidural space.
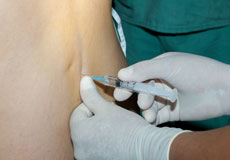
Epidural Steroid Injections
Epidural steroid injection (ESI) is a minimally invasive approach to treat inflammation of spinal nerves that causes pain in the neck, arms, back and legs. This technique may help relieve back pain in conditions such as spinal stenosis, spondylolysis or herniated discs.
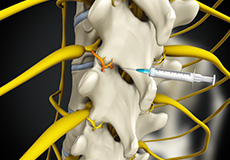
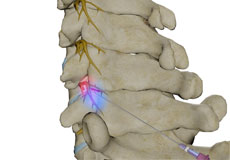
Facet Injections
The facet joints are the tiny joints situated at the upper and lower part of each vertebra, connecting one vertebra to the other. Each vertebra has four facet joints: a pair that connects to the vertebra above (superior facets) and another pair that connects to the vertebra below (inferior facets). They guide motion and provide stability.
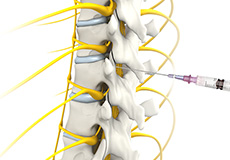
Spinal Nerve Blocks
A spinal nerve block is the injection of an anesthetic and steroid medication around the spinal nerve root to diagnose or treat pain.
Spine Injections
Spine injection is a non-surgical treatment modality recommended for the treatment of chronic back pain. Injection of certain medicinal agents relieves the pain by blocking the nerve signals between specific areas of the body and the brain.
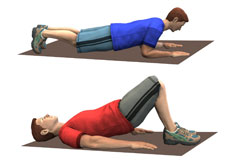
Physical therapy for the Spine
Physical therapy is one of the foremost necessary treatment modes of recovery for back pain. A referral to physiotherapy sometimes is created by your spine surgeon. A physical therapist is a well-trained, skilled health care professional who facilitates improving movement and manages the pain by safe stretching, conditioning, and strengthening exercise techniques.
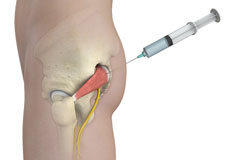
Piriformis Muscle Injection
The piriformis muscle is present in the buttocks, connecting the sacrum to the outer surface of the hip. This muscle enables us to walk and run. The sciatic nerve is a thick, long nerve passing through or below the piriformis muscle.
Costo-vertebral Joint Injection
Costo-vertebral joint injection, also known as a costovertebral block, is performed to alleviate upper back pain caused by damage or injury to the costovertebral joint. The costovertebral joint is located on either side of the vertebrae and connects the heads of the ribs with the vertebral bodies.
Non-Surgical Spine Treatments
In most cases, back pain can be resolved without surgery. The conservative treatment involves the use of pain medications and other methods to reduce inflammation and restore normal function. Usually, some self-care methods and medications can help to overcome back pain, but if pain and inflammation persist over 72 hours, it is necessary to consult your physician.
Non-Surgical Treatment for Disc Disease
The spinal column consists of vertebral bones stacked one on top of the other, surrounding and protecting the spinal cord. Soft cartilaginous discs present between the vertebrae support the spine, act as cushions against stress and permit spine mobility.
Anterior Cervical Discectomy with Fusion
Anterior cervical discectomy with fusion is an operative procedure to relieve compression or pressure on nerve roots and/or the spinal cord due to a herniated disc or bone spur in the neck. The vertebra is approached from the from (anterior) of your neck.
Cervical Disc Replacement
The cervical spine is located in the neck region and consists of seven bones arranged one on top of the other. Cushioning tissue called vertebral discs located between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers, allowing easy movement of the neck.
Cervical Spine Fusion
Cervical spine fusion is a surgery performed to fuse weak cervical vertebrae with adjacent vertebrae to provide stability and prevent injury to the spinal cord.
Cervical Arthroplasty
Arthroplasty is a surgical procedure to restore joint function by replacing a damaged joint with an artificial joint called a prosthesis.
Cervical/Lumbar Traction
Traction or spinal decompression therapy separates the vertebrae and reduces the pressure on the nerves.
Cervical Laminectomy
Laminectomy refers to the removal or cutting of the lamina (roof) of the vertebral bones to provide space for the nerves to exit from the spine.
Cervical Foraminotomy
Cervical foraminotomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve the symptoms of a pinched or compressed spinal nerve by enlarging the neural foramen, an opening for the nerve roots to exit the spine and travel through the body.
Cervical Laminoplasty
A cervical laminoplasty is an operative procedure that involves reshaping/repositioning the bone at the neck region (cervical spine) to relieve excess pressure on the spinal nerves. It can also be performed to relieve the symptoms of the narrowed spinal canal known as spinal stenosis.
Minimally Invasive Cervical Discectomy
A cervical discectomy or decompressive spinal procedure is an operative procedure that relieves pressure on the spinal nerves and/or spinal cord by partially or completely removing the intervertebral disc that is herniated and/or bony material (bone spur). Cervical discectomy can be performed using a minimally invasive approach if you are suitable.
Cervical Microdiscectomy
Your spine consists of 24 bones called vertebrae that are arranged one above the other and separated by intervertebral discs which act as shock absorbers during activity. Your neck or cervical area is made up of seven of these vertebrae. The intervertebral discs consist of 2 parts, namely annulus fibrosus (outer flexible ring) and nucleus pulposus (central soft jelly-like region).
Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion
Cervical laminectomy is a surgical procedure in which the spinal canal is made larger by removing the spinous process and the lamina in the cervical region of the spine. This reduces neck pain and relieves the pressure on the spinal cord caused by the degenerative changes in the intervertebral discs in the cervical region.
Posterior Cervical Microforaminotomy/Discectomy
Posterior cervical microforaminotomy/discectomy is an operative procedure that relieves pressure or compression on the nerve roots at the cervical spine.
Posterior Cervical Decompression
Posterior cervical decompression is a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck to relieve pressure over compressed nerves in the cervical spine region caused by inflamed spinal tissue or nerves, by removing portions of the cervical vertebrae.
Posterior Cervical Foraminotomy
Posterior cervical foraminotomy is a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck to relieve symptoms of a pinched or compressed spinal nerve by enlarging the neural foramen, an opening for the nerve roots to exit the spine and travel through the body, and creating more space for the spinal nerve to pass through.
Posterior Cervical Laminectomy and Fusion
Injury or wear-and-tear can cause parts of the cervical vertebrae in the neck region to compress the nerves of the spinal cord, leading to pain, numbness, or tingling in the part of the body that the nerve supplies.
Anterior Cervical Corpectomy and Fusion
An anterior cervical corpectomy and fusion is an operative procedure to relieve pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves by removing the vertebral bone and intervertebral disc material (decompression) in the cervical spine or neck.
Artificial Cervical Disc Replacement
Artificial cervical disc replacement is a spine surgery to replace a degenerated (deteriorated) disc in the neck with an artificial disc. The artificial disc, like the natural healthy disc, is used to replace the degenerated disc.
Cervical Corpectomy and Strut Graft
A cervical corpectomy and strut graft is a surgical procedure aimed at relieving the compression on the spinal cord by removing the degenerated vertebrae and replacing them with a bone graft.
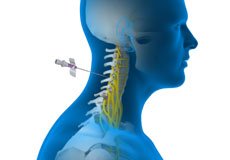
Cervical Epidurals
A cervical epidural is an injection of medication into the epidural space in the lower section of the cervical region to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back.
Cervical Bracing
Cervical braces are external devices used to provide support and restrict movement of the cervical spine in a variety of cervical conditions ranging from muscle spasm to severe spine instability or post-surgery.
Cervical Facet Blocks
A facet block is a procedure in which a combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid is injected into a facet joint. A cervical facet block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the neck.
Posterior Cervical Fusion
Posterior cervical fusion (PCF), a surgical procedure performed through the back of the neck, involves joining or fusing two or more damaged cervical vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae is also known as arthrodesis. Sometimes, metallic plates may be used for fixing the vertebrae, this is also known as instrumentation.
In-Office Cervical Injections
In-office cervical injections are administered in a medical office or clinic setting to provide relief from pain or inflammation affecting the neck and upper back.
Lumbar Artificial Disc Replacement
Lumbar artificial disc replacement is a surgical procedure employed to remove and replace a damaged or worn out disc in the lumbar or lower part of your spine that has become painful and debilitating with an artificial or synthetic disc.
Lumbar Facet Block
A facet block is a procedure in which a combination of a local anesthetic and a corticosteroid is injected into a facet joint. A lumbar facet block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the lower back.
Lumbar Epidurals
Lumbar epidurals are injections to treat and relieve low back pain. A lumbar epidural involves injecting a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory steroid into the epidural space of the lower spine (lower back) to reduce inflammation causing the pain.
Lumbar Radiculopathy
Back pain is a common condition affecting approximately 80% of the population at some point in their lives. The area usually affected is the lower back (lumbar region) as it bears most of the upper body’s weight. Trauma to the spine, age and overuse can result in deterioration of the vertebral bones and joints or bulging of the discs.
Lumbar Fusion
Spinal fusion, also called arthrodesis, is a surgical technique used to join two or more vertebrae (bones) within the spine. Lumbar fusion is the procedure of fusing the vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine (lower back).
Lumbar Laminectomy
Lumbar laminectomy is a spinal surgery to relieve excess pressure on the spinal cord or nerves within the spinal canal in the lumbar or lower back region. The pressure may be caused by bony overgrowths, herniated discs, injury, tumors, or narrowing of the spinal canal resulting in painful symptoms affecting a person’s ability to perform normal day to day activities.
Lumbar Foraminotomy
A lumbar foraminotomy is a surgical procedure that decompresses the spinal nerves by removing bone and other tissues that obstruct the neural foramen.
Lumbar Decompression
Lumbar decompression is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure over the compressed nerves in the lower spine (lumbar region).
Lumbar Endoscopic Discectomy
Lumbar endoscopic discectomy is a minimally invasive surgical procedure to treat a herniated or ruptured disc and relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
Lumbar Discectomy
A lumbar discectomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat a herniated or ruptured disc and relieve pressure on the spinal nerves.
Lower Back Pain Surgery
Lower back pain can be disabling; however, most cases heal with time (2-12 weeks) and with conservative therapy. However, surgery is suggested when symptoms persist and begin to affect your daily activities.
Lumbar Facetectomy and Foraminotomy
Facetectomy and foraminotomy are the most common spinal surgical procedures recommended for chronic pain due to spinal nerve compression. Lumbar foraminotomy is a decompression surgery involving the removal of bone and tissue obstructing the neuroforamen to release the pressure on the spinal nerve roots.
Lumbar Microdiscectomy
Microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure employed to relieve the pressure over the spinal cord and/or nerve roots, caused by a ruptured (herniated) intervertebral disc. A herniated disc, common in the lower back (lumbar spine) occurs when the inner gelatinous substance of the disc escapes through a tear in the outer, fibrous ring (annulus fibrosis).
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Discectomy
Lumbar discectomy is a spinal surgery that involves the removal of the damaged intervertebral disc(s) to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region, which forms the lower portion of the spine and comprises of five vertebrae (L1-L5). A minimally invasive technique is implemented to perform the surgery.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Surgery
Spinal surgery can be performed by two different approaches; one is the conventional open surgical approach and the other is the advanced minimally invasive approach. Each approach has its own advantages and preferences. However, the minimally invasive technique is a more advanced approach with a higher success rate and a minimal level of patient discomfort.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Decompression
Minimally invasive lumbar decompression or mild® is a procedure developed by Vertos Medical to treat lumbar spinal stenosis by relieving pressure on the spinal nerves.
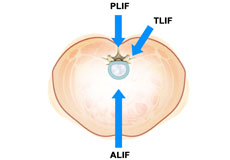
Minimally Invasive TLIF
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a minimally invasive fusion of the vertebrae of the lumbar region (lower back). It is designed to provide stability to the spine and treat back and leg pain.
Radiofrequency Ablation for Lumbar Spondylosis
Radiofrequency ablation for lumbar spondylosis is a minimally invasive surgical procedure performed to treat lower back pain secondary to lumbar spondylosis. The procedure employs radiofrequency waves to produce heat which damages the nerves transmitting pain signals to the brain in the lumbar spine.
Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion (TLIF)
Transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion (TLIF) is a type of spinal fusion procedure in which bone graft is placed between the affected vertebrae in the lower back (lumbar) region through an incision on the patient’s back.
Lumbar Corpectomy and Fusion
Lumbar corpectomy and fusion is a surgical technique performed to remove the vertebral bone or disc material between the vertebrae to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region.
Oblique Lumbar Interbody Fusion (OLIF)
Lumbar interbody fusion can be performed through different approaches. Oblique lumbar interbody fusion (OLIF) is a minimally invasive approach to LIF, where an incision is made on your side to avoid damaging important muscles and ligaments in your back.
Minimally Invasive Lumbar Fusion
A minimally invasive lumbar fusion technique is used to treat fractured vertebra, lumbar instability, spine deformities – scoliosis or kyphosis, cervical disc hernias, tumors, back pain, and failed back syndrome. Spondylolisthesis, a painful condition of the spine caused by disc displacement or slipped disc, can be treated with minimally invasive lumbar fusion technique.
Anterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) is a surgery performed to correct spinal problems in the lower back. The surgery can be implemented either as an open surgery or minimally invasive technique.
Anterior Lumbar Corpectomy and Fusion
Anterior Lumbar Corpectomy and Fusion is a surgical technique performed to remove the vertebral bone or disc material between the vertebrae to alleviate pressure on the spinal cord and spinal nerves (decompression) in the lumbar (lower back) region.
Lateral Lumbar Interbody Fusion
The back is made up of a number of small bones called vertebrae. Cushioning discs present between the vertebrae act as shock absorbers. The vertebral column allows the cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers called the spinal cord to pass through the entire column length and branch out to the various parts of the body.
Posterolateral Lumbar Fusion
Posterolateral lumbar fusion is a surgical technique that involves correcting spinal problems from the back of the spine by placing bone graft between segments in the back and leaving the disc space intact.
Posterior Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Spinal fusion is a surgical technique that joins two or more vertebrae in the spine to minimize the pain caused by the movement of these vertebrae. The fusion of vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine is called lumbar fusion. This surgery can be performed as an open or minimally invasive procedure.
Posterior Lumbar Fusion
Spinal fusion, also called arthrodesis, is a surgical technique used to join two or more vertebrae (bones) within the spine. Lumbar fusion is the fusion the vertebrae in the lumbar portion of the spine (lower back).
Lumbar Spinal Fusion
The surgical technique of combining two or more vertebrae is known as spinal fusion. Back pain due to abnormal motion of the vertebrae is treated by this procedure.
Lumbar Interbody Fusion
Lumbar interbody fusion (LIF) surgery is a surgical technique that involves the removal of a damaged intervertebral disc and the insertion of a bone graft into the disc space created between the two adjoining vertebrae. Bone grafts promote healing and facilitate fusion. Screws and rods are used to stabilize the spine during the healing process.
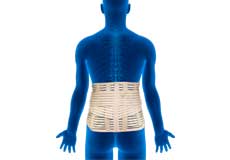
Lumbar Spinal Bracing
Lumbar braces are external devices used to restrict the movement of the lumbar spine and provide support and stability to the lower back region, to relieve back pain and promote healing after surgery or injury.
Lumbar Medial Branch Block
A medial branch block is a procedure in which a mixture of a local anesthetic with or without a corticosteroid is injected near the medial branch nerves supplying a facet joint. A lumbar medial branch block prevents the transmission of pain signals from the lower back.
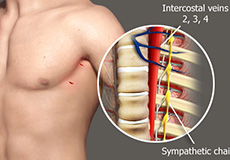
Lumbar Sympathetic Block
A lumbar sympathetic block is an injection of a local anesthetic and steroid that is injected into or around the sympathetic nerves to block the transmission of pain impulses from the legs or lower back, thereby relieving pain.
In-Office Lumbar Injections
In-office lumbar injections are steroid shots administered to you in your physician’s clinical or office setting to relieve low back pain. These shots involve injecting a local anesthetic and an anti-inflammatory steroid into the lumbar (lower back) area of your spine.
Thoracic Discectomy
The human spine provides support to the body allowing you to stand upright, bend, and twist. The spine can be broadly divided into the cervical, thoracic, and lumbar spine. The thoracic spine lies in the mid-back region between the neck and lower back and is protected by the rib cage.
Thoracic Corpectomy
Thoracic corpectomy is a surgical procedure performed to relieve pressure on a nerve at the thoracic region (upper and middle back) by removing the source of the compression.
Thoracic Laminectomy
The vertebral column supports the back and protects the spinal cord that runs through it. The nerves that branch out from the spinal cord are also protected and pass through special passages created by each vertebral bone. However, degeneration or herniation (bulging out) of the intervertebral disc that cushions each vertebral bone, injury, bony outgrowths due to arthritis or tumors can compress the spinal cord and nerves, causing debilitating back pain and disability.
Thoracic Vertebrectomy
The spinal cord passes through the vertebral column, which forms a bony protective cover. However, a spinal tumor can compress the spinal cord or spinal nerves, leading to pain, loss of sensation, and/or motor function in the part of the body supplied by the compressed nerve.
Thoracic Spine Decompression
Thoracic spine decompression is a procedure to relieve pressure on the spinal nerves in the middle portion of the back. Spine decompression surgery is indicated in treating spinal stenosis. Spinal stenosis is the narrowing of the spinal canal caused by degeneration of the facet joints and the thickening of the ligaments.
Thoracic Spine Fracture Repair Surgery
Spinal fractures occur most commonly in the thoracic (upper back) and lumbar (lower back) regions, and at the thoracolumbar junction. Fractures in these regions can occur due to injury from falls, motor vehicle accidents, violent acts and sports accidents, and also from the degeneration of bones due to old age and disease (osteoporosis and tumors).
Thoracic Spine Revision Surgery
Revision spine surgery is performed to correct the problems of earlier spine surgery. It is considered when you do not obtain relief from pain following the initial surgery.
Posterior Thoracic Fusion
Posterior thoracic fusion is a spinal fusion procedure performed through an incision on the back (posterior) of the patient in which two or more vertebrae of the thoracic spine (mid back) are joined together, eliminating any movement between them.
Thoracic Vertebroplasty
Osteoporosis is a “silent” disease characterized by weakening of bones, making them more susceptible to fractures (vertebral compression fractures), typically in the hip and spine. Vertebral compression fractures can also occur with a metastatic tumor, multiple myeloma, and vertebral hemangioma.
Computer Navigated Thoracic Spine Surgery
The spine is a complex 3- dimensional structure that is interspersed with a complex lattice of delicate blood vessels and nerves. Trauma to these structures during surgery is a big concern in spinal surgery. The complexity and increased need for precision in thoracic spine surgeries have led to the introduction of computers to assist in many spinal procedures.
Thoracic Facet Joint Injection
Facet joints are small joints present between the vertebral bones including the vertebral bones of the thorax (upper back). The bones in these joints are covered by cartilage and a capsule filled with synovial fluid surrounds the joint reducing friction.
Microdiscectomy
The spine is made up of small bony segments called vertebrae. These vertebrae are categorized into cervical or neck vertebrae, thoracic or upper back vertebrae, lumbar or lower back vertebrae and the sacrum within the pelvis.
Spine Medications
Medications play an effective role in the treatment of back or neck pain. Your doctor may prescribe several medications to help reduce pain and associated symptoms that are caused by unhealthy spinal conditions or deformities.
Back Pain Exercises
Strenuous activities of daily living can stress the back resulting in pain. It is natural at this time to withdraw from activity and rest, but is not helpful in the long run and may actually slow down the healing process.
Spine Rehabilitation
Dysfunction of the spine can be severely debilitating to one’s ability to perform activities at both home and work. Pain in the lumbar spine (lower back) is the number one reason for missed days of work, followed by the pain of the cervical spine (neck).
Preventing Back Pain at Home and Work
When lifting objects, try to bend at the knees instead of the waist and let your legs do the lifting, not your back. Keep the object close to your body. Know your limits and get help if you feel it is too heavy. The way you sleep can also affect the health of your back. Use a firm mattress, check for wear-and-tear, and change it regularly.
Back and Neck Braces
The spine is composed of spinal bones called vertebrae, intervertebral discs, connective tissue, and muscles. All of these structures provide support, stability, and mobility to the upper body. The spine also protects the delicate spinal cord. Injury or disease to any of these structures can cause pain.
Nutrition and Your Spine
Nutrients are the chemical components present in food, which provide energy for carrying out normal physiological functions and aid in various metabolic processes of the body.
Recovery and Post-op Instructions after Spine Surgery
The duration of hospitalization depends on the treatment rendered. The period of your rest or inactivity depends on a few factors such as the type of surgical procedure and the approach used to access your hip, the size of the incision and presence of any complications.
Spine Comprehensive Medicine
Spine comprehensive medicine involves comprehensive care of acute or chronic neck or back injuries or conditions. It aims at minimizing your pain, making you as functional as possible and preventing future injury.
Healthy Back Tips
Back and neck pain is the most common health problems experienced by most people, at some point in their lives. People with back pain or neck pain may have trouble performing daily routine activities.
Proper Lifting
Lifting heavy weights and improper lifting of weights is one of the foremost causes of neck pain or lower back pain. Practicing proper lifting techniques is essential to avoid strain on your neck and back.
Am I a Candidate for Spine Surgery?
Spinal issues manifest in a large number of people at all phases of life. Back pain is one of the most common complaints that individuals visit a doctor for. Many orthopedic issues such as arthritis and other joint problems are manifested in the spine.
Complications of Spinal Surgery
The most serious complication of a herniated disc that may occur before surgery is the development of the cauda equine syndrome. It occurs when a large particle of disc material ruptures in the spinal canal. It occurs in the area where the nerves that control the bowels and bladder travel before they leave the spine.
Lumbar Spine Anatomy
The spine also called the back bone, plays a vital role in stability, smooth movement and protection of the delicate spinal cord. It is made up of bony segments called vertebra with fibrous tissue called intervertebral discs between them. The vertebra and discs form the spinal column from the head to the pelvis, giving symmetry and support to the body.
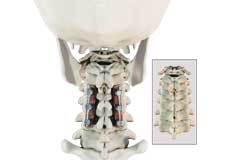
Cervical Spine Anatomy
The spine can be divided into 4 parts: cervical, thoracic, lumbar and sacral region. The cervical spine comprises of the first 7 vertebrae, which form the neck.
Thoracic Spine Anatomy
The thoracic spine is the central part of the spine, also called the dorsal spine, which runs from the base of the neck to the bottom of your rib cage. The thoracic spine provides the flexibility that holds the body upright and protects the organs of the chest.